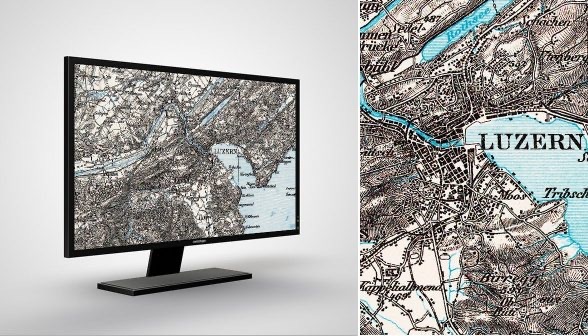
The Dufour map: a masterpiece of cartography and testimony to a nation in the making
In 1848, Switzerland was given a new constitution. It laid the foundation for the modern federal state that replaced the previous confederation of cantons. This was graphically illustrated by the Dufour Map, the first official map series. To mark the 175th anniversary of the Federal Constitution, the Federal Office of Topography swisstopo is making the first edition of the Dufour Map digitally available.
Diesen Beitrag auf Deutsch lesen 🇩🇪
The Dufour Map is the first official map to depict the new federal state that was founded in 1848 with the Federal Constitution. It shows for the first time a «united Switzerland». The cantonal borders, often prominent lines on older maps, faded into the background in favour of the national border. The cooperation across all cantons allowed for a uniform representation. The map shows a self-contained representation of a nation in the making. In this way, the Dufour map prominently illustrates the change from a confederation of states to a federal state 175 years ago.
To the map viewer on map.geo.admin.ch: Dufour map
The Dufour map is also a masterpiece of cartography: the terrain is depicted with oblique hachures assuming northwest illumination. This made the relief and rock drawing appear particularly vivid, a great advantage for the mountainous Swiss landscape. This so-called «Swiss style» earned the Topographical Bureau, which later became the Federal Office of Topography (swisstopo), much praise and several international awards.

Individual sheets of the Dufour map for download
| The cantons had already begun surveying the land in 1809 as part of military cooperation. The triangulation of the Swiss Plateau progressed rapidly, while that of the Alps was more difficult due to the dangerous mountains and bad weather conditions with poor visibility. In 1832, Guillaume Henri Dufour was appointed Quartermaster General of the Military Inspectorate and took charge of the federal triangulation and national survey. In 1838, the Federal Topographical Bureau officially began its work in Geneva, making 1838 the founding year of today’s Federal Office of Topography (swisstopo). In 1842, Dufour published the Geneva map, which served as a test piece. The other sheets were produced between 1845 and 1865 at a scale of 1:100,000 and updated until 1939. Henri Dufour played a significant role in Swiss history not only as a cartographer, but also as an engineer, politician, general and humanist. Among other things, he was a co-founder of the Swiss Red Cross. During his lifetime, the Swiss Federal Council named the highest peak in the Valais Alps and in Switzerland after him, the Dufourspitze (4634 metres above sea level). |

Dufour Map (Source: swisstopo admin.ch)
- Official name: Topographische Karte der Schweiz (no official English name)
- Reference system: CH1840
- Projection: Equivalent conical projection
- Point of origin for height measurements: Repère Pierre du Niton 376,2 m above sea level = ‹old horizon›
Production
- Method of ground representation: obliquely luminated hachures
- Method of reproduction: copperplate engraving
- Method of printing: intaglio printing (from 1905 also planographic printing)
- Colors: 1 (from 1908: 2, from 1938: 3)
- Map format: 70 x 48 cm = 3360 km2
- Number of sheets: 25
- First edition: 1845-1865
- Revision: until 1939
Would you like to know more about the history of the Dufour Map?
«swisstopo historic» has compiled 28 interesting stories about the Dufour Map (in German).

Monika Kriemler Fritsche, Liaison Librarian Geography, University Library Zurich
